How-To: Invoke services using HTTP
This article demonstrates how to deploy services each with an unique application ID for other services to discover and call endpoints on them using service invocation over HTTP.
Note
If you haven’t already, try out the service invocation quickstart for a quick walk-through on how to use the service invocation API.Choose an ID for your service
Dapr allows you to assign a global, unique ID for your app. This ID encapsulates the state for your application, regardless of the number of instances it may have.
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3500 -- python3 checkout/app.py
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 8001 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3501 -- python3 order-processor/app.py
If your app uses a TLS, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over a TLS connection by setting --app-protocol https:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-protocol https --dapr-http-port 3500 -- python3 checkout/app.py
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 8001 --app-protocol https --dapr-http-port 3501 -- python3 order-processor/app.py
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3500 -- npm start
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 5001 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3501 -- npm start
If your app uses a TLS, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over a TLS connection by setting --app-protocol https:
dapr run --app-id checkout --dapr-http-port 3500 --app-protocol https -- npm start
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 5001 --dapr-http-port 3501 --app-protocol https -- npm start
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3500 -- dotnet run
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 7001 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3501 -- dotnet run
If your app uses a TLS, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over a TLS connection by setting --app-protocol https:
dapr run --app-id checkout --dapr-http-port 3500 --app-protocol https -- dotnet run
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 7001 --dapr-http-port 3501 --app-protocol https -- dotnet run
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3500 -- java -jar target/CheckoutService-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 9001 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3501 -- java -jar target/OrderProcessingService-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
If your app uses a TLS, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over a TLS connection by setting --app-protocol https:
dapr run --app-id checkout --dapr-http-port 3500 --app-protocol https -- java -jar target/CheckoutService-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 9001 --dapr-http-port 3501 --app-protocol https -- java -jar target/OrderProcessingService-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
dapr run --app-id checkout --dapr-http-port 3500 -- go run .
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 6006 --app-protocol http --dapr-http-port 3501 -- go run .
If your app uses a TLS, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over a TLS connection by setting --app-protocol https:
dapr run --app-id checkout --dapr-http-port 3500 --app-protocol https -- go run .
dapr run --app-id order-processor --app-port 6006 --dapr-http-port 3501 --app-protocol https -- go run .
Set an app-id when deploying to Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, set the dapr.io/app-id annotation on your pod:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: <language>-app
namespace: default
labels:
app: <language>-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: <language>-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: <language>-app
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/app-id: "order-processor"
dapr.io/app-port: "6001"
...
If your app uses a TLS connection, you can tell Dapr to invoke your app over TLS with the app-protocol: "https" annotation (full list here). Note that Dapr does not validate TLS certificates presented by the app.
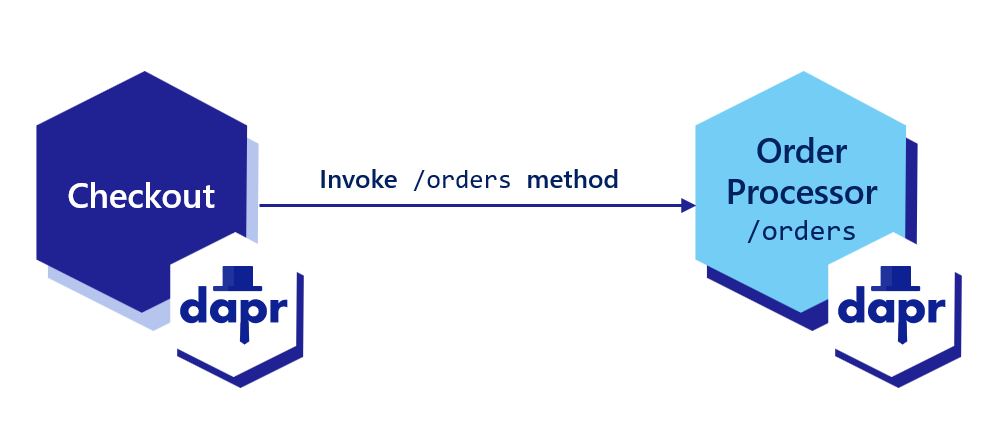
Invoke the service
To invoke an application using Dapr, you can use the invoke API on any Dapr instance. The sidecar programming model encourages each application to interact with its own instance of Dapr. The Dapr sidecars discover and communicate with one another.
Below are code examples that leverage Dapr SDKs for service invocation.
#dependencies
import random
from time import sleep
import logging
import requests
#code
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO)
while True:
sleep(random.randrange(50, 5000) / 1000)
orderId = random.randint(1, 1000)
#Invoke a service
result = requests.post(
url='%s/orders' % (base_url),
data=json.dumps(order),
headers=headers
)
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO)
logging.info('Order requested: ' + str(orderId))
logging.info('Result: ' + str(result))
//dependencies
import axios from "axios";
//code
const daprHost = "127.0.0.1";
var main = function() {
for(var i=0;i<10;i++) {
sleep(5000);
var orderId = Math.floor(Math.random() * (1000 - 1) + 1);
start(orderId).catch((e) => {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
});
}
}
//Invoke a service
const result = await axios.post('order-processor' , "orders/" + orderId , axiosConfig);
console.log("Order requested: " + orderId);
console.log("Result: " + result.config.data);
function sleep(ms) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
main();
//dependencies
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Threading;
//code
namespace EventService
{
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
while(true) {
await Task.Delay(5000)
var random = new Random();
var orderId = random.Next(1,1000);
//Using Dapr SDK to invoke a method
var order = new Order(orderId.ToString());
var httpClient = DaprClient.CreateInvokeHttpClient();
var response = await httpClient.PostAsJsonAsync("http://order-processor/orders", order);
var result = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine("Order requested: " + orderId);
Console.WriteLine("Result: " + result);
}
}
}
}
//dependencies
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//code
@SpringBootApplication
public class CheckoutServiceApplication {
private static final HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.version(HttpClient.Version.HTTP_2)
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.build();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
while (true) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5000);
Random random = new Random();
int orderId = random.nextInt(1000 - 1) + 1;
// Create a Map to represent the request body
Map<String, Object> requestBody = new HashMap<>();
requestBody.put("orderId", orderId);
// Add other fields to the requestBody Map as needed
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(new JSONObject(requestBody).toString()))
.uri(URI.create(dapr_url))
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("dapr-app-id", "order-processor")
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
System.out.println("Order passed: " + orderId);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
log.info("Order requested: " + orderId);
log.info("Result: " + response.body());
}
}
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
daprHttpPort := os.Getenv("DAPR_HTTP_PORT")
if daprHttpPort == "" {
daprHttpPort = "3500"
}
client := &http.Client{
Timeout: 15 * time.Second,
}
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
time.Sleep(5000)
orderId := rand.Intn(1000-1) + 1
url := fmt.Sprintf("http://localhost:%s/checkout/%v", daprHttpPort, orderId)
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, url, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// Adding target app id as part of the header
req.Header.Add("dapr-app-id", "order-processor")
// Invoking a service
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err.Error())
}
b, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(string(b))
}
}
Additional URL formats
To invoke a ‘GET’ endpoint:
curl http://localhost:3602/v1.0/invoke/checkout/method/checkout/100
To avoid changing URL paths as much as possible, Dapr provides the following ways to call the service invocation API:
- Change the address in the URL to
localhost:<dapr-http-port>. - Add a
dapr-app-idheader to specify the ID of the target service, or alternatively pass the ID via HTTP Basic Auth:http://dapr-app-id:<service-id>@localhost:3602/path.
For example, the following command:
curl http://localhost:3602/v1.0/invoke/checkout/method/checkout/100
is equivalent to:
curl -H 'dapr-app-id: checkout' 'http://localhost:3602/checkout/100' -X POST
or:
curl 'http://dapr-app-id:checkout@localhost:3602/checkout/100' -X POST
Using CLI:
dapr invoke --app-id checkout --method checkout/100
Including a query string in the URL
You can also append a query string or a fragment to the end of the URL and Dapr will pass it through unchanged. This means that if you need to pass some additional arguments in your service invocation that aren’t part of a payload or the path, you can do so by appending a ? to the end of the URL, followed by the key/value pairs separated by = signs and delimited by &. For example:
curl 'http://dapr-app-id:checkout@localhost:3602/checkout/100?basket=1234&key=abc' -X POST
Namespaces
When running on namespace supported platforms, you include the namespace of the target app in the app ID. For example, following the <app>.<namespace> format, use checkout.production.
Using this example, invoking the service with a namespace would look like:
curl http://localhost:3602/v1.0/invoke/checkout.production/method/checkout/100 -X POST
See the Cross namespace API spec for more information on namespaces.
View traces and logs
Our example above showed you how to directly invoke a different service running locally or in Kubernetes. Dapr:
- Outputs metrics, tracing, and logging information,
- Allows you to visualize a call graph between services and log errors, and
- Optionally, log the payload body.
For more information on tracing and logs, see the observability article.
Related Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.