How to: Publish a message and subscribe to a topic
Now that you’ve learned what the Dapr pub/sub building block provides, learn how it can work in your service. The below code example loosely describes an application that processes orders with two services, each with Dapr sidecars:
- A checkout service using Dapr to subscribe to the topic in the message queue.
- An order processing service using Dapr to publish a message to RabbitMQ.
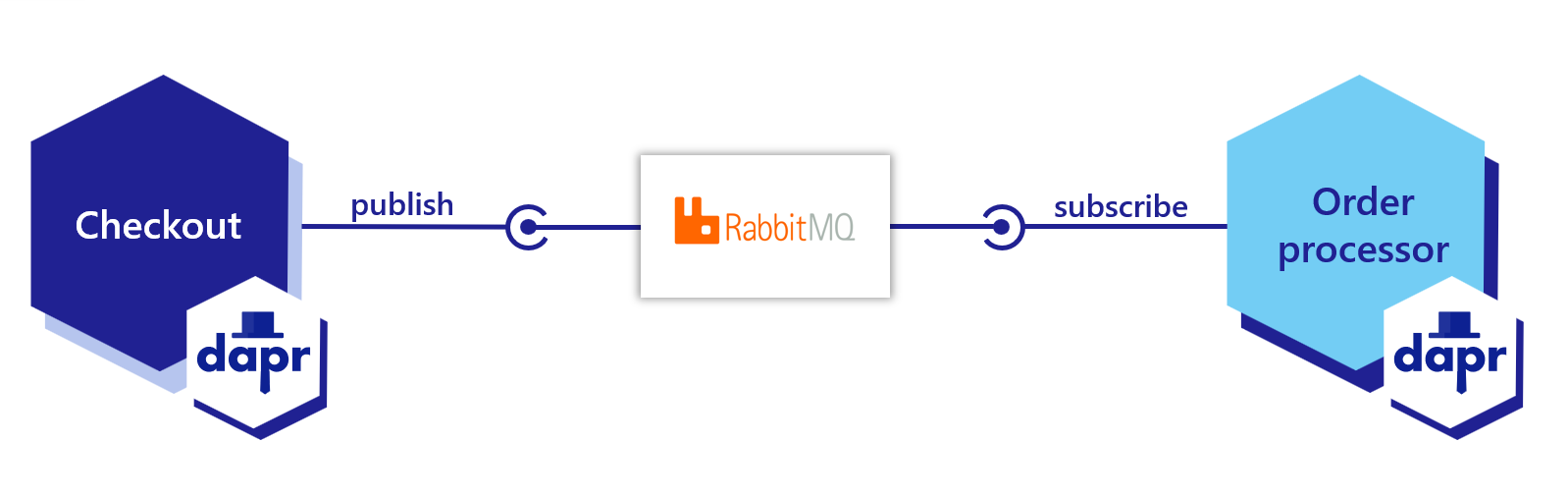
Dapr automatically wraps the user payload in a CloudEvents v1.0 compliant envelope, using Content-Type header value for datacontenttype attribute. Learn more about messages with CloudEvents.
The following example demonstrates how your applications publish and subscribe to a topic called orders.
Note
If you haven’t already, try out the pub/sub quickstart for a quick walk-through on how to use pub/sub.Set up the Pub/Sub component
The first step is to set up the pub/sub component:
When you run dapr init, Dapr creates a default Redis pubsub.yaml and runs a Redis container on your local machine, located:
- On Windows, under
%UserProfile%\.dapr\components\pubsub.yaml - On Linux/MacOS, under
~/.dapr/components/pubsub.yaml
With the pubsub.yaml component, you can easily swap out underlying components without application code changes. In this example, RabbitMQ is used.
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: order-pub-sub
spec:
type: pubsub.rabbitmq
version: v1
metadata:
- name: host
value: "amqp://localhost:5672"
- name: durable
value: "false"
- name: deletedWhenUnused
value: "false"
- name: autoAck
value: "false"
- name: reconnectWait
value: "0"
- name: concurrency
value: parallel
scopes:
- orderprocessing
- checkout
You can override this file with another pubsub component by creating a components directory (in this example, myComponents) containing the file and using the flag --resources-path with the dapr run CLI command.
dapr run --app-id myapp --resources-path ./myComponents -- dotnet run
dapr run --app-id myapp --resources-path ./myComponents -- mvn spring-boot:run
dapr run --app-id myapp --resources-path ./myComponents -- python3 app.py
dapr run --app-id myapp --resources-path ./myComponents -- go run app.go
dapr run --app-id myapp --resources-path ./myComponents -- npm start
To deploy this into a Kubernetes cluster, fill in the metadata connection details of the pub/sub component in the YAML below, save as pubsub.yaml, and run kubectl apply -f pubsub.yaml.
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: order-pub-sub
spec:
type: pubsub.rabbitmq
version: v1
metadata:
- name: connectionString
value: "amqp://localhost:5672"
- name: protocol
value: amqp
- name: hostname
value: localhost
- name: username
value: username
- name: password
value: password
- name: durable
value: "false"
- name: deletedWhenUnused
value: "false"
- name: autoAck
value: "false"
- name: reconnectWait
value: "0"
- name: concurrency
value: parallel
scopes:
- orderprocessing
- checkout
Subscribe to topics
Dapr provides three methods by which you can subscribe to topics:
- Declaratively, where subscriptions are defined in an external file.
- Streaming, where subscriptions are defined in user code.
- Programmatically, where subscriptions are defined in user code.
Learn more in the declarative, streaming, and programmatic subscriptions doc. This example demonstrates a declarative subscription.
Create a file named subscription.yaml and paste the following:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v2alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: order-pub-sub
spec:
topic: orders
routes:
default: /checkout
pubsubname: order-pub-sub
scopes:
- orderprocessing
- checkout
The example above shows an event subscription to topic orders, for the pubsub component order-pub-sub.
- The
routefield tells Dapr to send all topic messages to the/checkoutendpoint in the app. - The
scopesfield enables this subscription for apps with IDsorderprocessingandcheckout.
Place subscription.yaml in the same directory as your pubsub.yaml component. When Dapr starts up, it loads subscriptions along with the components.
Note
This feature is currently in preview. Dapr can be made to “hot reload” declarative subscriptions, whereby updates are picked up automatically without needing a restart. This is enabled by via theHotReload feature gate.
To prevent reprocessing or loss of unprocessed messages, in-flight messages between Dapr and your application are unaffected during hot reload events.
Below are code examples that leverage Dapr SDKs to subscribe to the topic you defined in subscription.yaml.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Dapr;
using Dapr.Client;
namespace CheckoutService.Controllers;
[ApiController]
public sealed class CheckoutServiceController : ControllerBase
{
//Subscribe to a topic called "orders" from the "order-pub-sub" compoennt
[Topic("order-pub-sub", "orders")]
[HttpPost("checkout")]
public void GetCheckout([FromBody] int orderId)
{
Console.WriteLine("Subscriber received : " + orderId);
}
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the subscriber application:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-port 6002 --dapr-http-port 3602 --dapr-grpc-port 60002 --app-protocol https dotnet run
//dependencies
import io.dapr.Topic;
import io.dapr.client.domain.CloudEvent;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
//code
@RestController
public class CheckoutServiceController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CheckoutServiceController.class);
//Subscribe to a topic
@Topic(name = "orders", pubsubName = "order-pub-sub")
@PostMapping(path = "/checkout")
public Mono<Void> getCheckout(@RequestBody(required = false) CloudEvent<String> cloudEvent) {
return Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
try {
log.info("Subscriber received: " + cloudEvent.getData());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the subscriber application:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-port 6002 --dapr-http-port 3602 --dapr-grpc-port 60002 mvn spring-boot:run
#dependencies
from cloudevents.sdk.event import v1
from dapr.ext.grpc import App
import logging
import json
#code
app = App()
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO)
#Subscribe to a topic
@app.subscribe(pubsub_name='order-pub-sub', topic='orders')
def mytopic(event: v1.Event) -> None:
data = json.loads(event.Data())
logging.info('Subscriber received: ' + str(data))
app.run(6002)
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the subscriber application:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-port 6002 --dapr-http-port 3602 --app-protocol grpc -- python3 CheckoutService.py
//dependencies
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"context"
"github.com/dapr/go-sdk/service/common"
daprd "github.com/dapr/go-sdk/service/http"
)
//code
var sub = &common.Subscription{
PubsubName: "order-pub-sub",
Topic: "orders",
Route: "/checkout",
}
func main() {
s := daprd.NewService(":6002")
//Subscribe to a topic
if err := s.AddTopicEventHandler(sub, eventHandler); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error adding topic subscription: %v", err)
}
if err := s.Start(); err != nil && err != http.ErrServerClosed {
log.Fatalf("error listenning: %v", err)
}
}
func eventHandler(ctx context.Context, e *common.TopicEvent) (retry bool, err error) {
log.Printf("Subscriber received: %s", e.Data)
return false, nil
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the subscriber application:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-port 6002 --dapr-http-port 3602 --dapr-grpc-port 60002 go run CheckoutService.go
//dependencies
import { DaprServer, CommunicationProtocolEnum } from '@dapr/dapr';
//code
const daprHost = "127.0.0.1";
const serverHost = "127.0.0.1";
const serverPort = "6002";
start().catch((e) => {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
});
async function start(orderId) {
const server = new DaprServer({
serverHost,
serverPort,
communicationProtocol: CommunicationProtocolEnum.HTTP,
clientOptions: {
daprHost,
daprPort: process.env.DAPR_HTTP_PORT,
},
});
//Subscribe to a topic
await server.pubsub.subscribe("order-pub-sub", "orders", async (orderId) => {
console.log(`Subscriber received: ${JSON.stringify(orderId)}`)
});
await server.start();
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the subscriber application:
dapr run --app-id checkout --app-port 6002 --dapr-http-port 3602 --dapr-grpc-port 60002 npm start
Publish a message
Start an instance of Dapr with an app-id called orderprocessing:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --dapr-http-port 3601
Then publish a message to the orders topic:
dapr publish --publish-app-id orderprocessing --pubsub order-pub-sub --topic orders --data '{"orderId": "100"}'
curl -X POST http://localhost:3601/v1.0/publish/order-pub-sub/orders -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"orderId": "100"}'
Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -ContentType 'application/json' -Body '{"orderId": "100"}' -Uri 'http://localhost:3601/v1.0/publish/order-pub-sub/orders'
Below are code examples that leverage Dapr SDKs to publish a topic.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Dapr.Client;
using System.Threading;
const string PUBSUB_NAME = "order-pub-sub";
const string TOPIC_NAME = "orders";
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddDaprClient();
var app = builder.Build();
var random = new Random();
var client = app.Services.GetRequiredService<DaprClient>();
while(true) {
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5));
var orderId = random.Next(1,1000);
var source = new CancellationTokenSource();
var cancellationToken = source.Token;
//Using Dapr SDK to publish a topic
await client.PublishEventAsync(PUBSUB_NAME, TOPIC_NAME, orderId, cancellationToken);
Console.WriteLine("Published data: " + orderId);
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the publisher application:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --app-port 6001 --dapr-http-port 3601 --dapr-grpc-port 60001 --app-protocol https dotnet run
//dependencies
import io.dapr.client.DaprClient;
import io.dapr.client.DaprClientBuilder;
import io.dapr.client.domain.Metadata;
import static java.util.Collections.singletonMap;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//code
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderProcessingServiceApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderProcessingServiceApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
String MESSAGE_TTL_IN_SECONDS = "1000";
String TOPIC_NAME = "orders";
String PUBSUB_NAME = "order-pub-sub";
while(true) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5000);
Random random = new Random();
int orderId = random.nextInt(1000-1) + 1;
DaprClient client = new DaprClientBuilder().build();
//Using Dapr SDK to publish a topic
client.publishEvent(
PUBSUB_NAME,
TOPIC_NAME,
orderId,
singletonMap(Metadata.TTL_IN_SECONDS, MESSAGE_TTL_IN_SECONDS)).block();
log.info("Published data:" + orderId);
}
}
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the publisher application:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --app-port 6001 --dapr-http-port 3601 --dapr-grpc-port 60001 mvn spring-boot:run
#dependencies
import random
from time import sleep
import requests
import logging
import json
from dapr.clients import DaprClient
#code
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO)
while True:
sleep(random.randrange(50, 5000) / 1000)
orderId = random.randint(1, 1000)
PUBSUB_NAME = 'order-pub-sub'
TOPIC_NAME = 'orders'
with DaprClient() as client:
#Using Dapr SDK to publish a topic
result = client.publish_event(
pubsub_name=PUBSUB_NAME,
topic_name=TOPIC_NAME,
data=json.dumps(orderId),
data_content_type='application/json',
)
logging.info('Published data: ' + str(orderId))
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the publisher application:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --app-port 6001 --dapr-http-port 3601 --app-protocol grpc python3 OrderProcessingService.py
//dependencies
import (
"context"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
"strconv"
dapr "github.com/dapr/go-sdk/client"
)
//code
var (
PUBSUB_NAME = "order-pub-sub"
TOPIC_NAME = "orders"
)
func main() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
time.Sleep(5000)
orderId := rand.Intn(1000-1) + 1
client, err := dapr.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer client.Close()
ctx := context.Background()
//Using Dapr SDK to publish a topic
if err := client.PublishEvent(ctx, PUBSUB_NAME, TOPIC_NAME, []byte(strconv.Itoa(orderId)));
err != nil {
panic(err)
}
log.Println("Published data: " + strconv.Itoa(orderId))
}
}
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the publisher application:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --app-port 6001 --dapr-http-port 3601 --dapr-grpc-port 60001 go run OrderProcessingService.go
//dependencies
import { DaprServer, DaprClient, CommunicationProtocolEnum } from '@dapr/dapr';
const daprHost = "127.0.0.1";
var main = function() {
for(var i=0;i<10;i++) {
sleep(5000);
var orderId = Math.floor(Math.random() * (1000 - 1) + 1);
start(orderId).catch((e) => {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
});
}
}
async function start(orderId) {
const PUBSUB_NAME = "order-pub-sub"
const TOPIC_NAME = "orders"
const client = new DaprClient({
daprHost,
daprPort: process.env.DAPR_HTTP_PORT,
communicationProtocol: CommunicationProtocolEnum.HTTP
});
console.log("Published data:" + orderId)
//Using Dapr SDK to publish a topic
await client.pubsub.publish(PUBSUB_NAME, TOPIC_NAME, orderId);
}
function sleep(ms) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
main();
Navigate to the directory containing the above code, then run the following command to launch both a Dapr sidecar and the publisher application:
dapr run --app-id orderprocessing --app-port 6001 --dapr-http-port 3601 --dapr-grpc-port 60001 npm start
Message acknowledgement and retries
In order to tell Dapr that a message was processed successfully, return a 200 OK response. If Dapr receives any other return status code than 200, or if your app crashes, Dapr will attempt to redeliver the message following at-least-once semantics.
Demo video
Watch this demo video to learn more about pub/sub messaging with Dapr.
Next steps
- Try the pub/sub tutorial.
- Learn about messaging with CloudEvents and when you might want to send messages without CloudEvents.
- Review the list of pub/sub components.
- Read the API reference.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.