Using Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector to collect traces to send to Dynatrace
Dapr integrates with the Dynatrace Collector using the OpenTelemetry protocol (OTLP). This guide walks through an example using Dapr to push traces to Dynatrace, using the Dynatrace version of the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Note
This guide refers to the Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector, which uses the same Helm chart as the open-source collector but overridden with the Dynatrace-maintained image for better support and Dynatrace-specific features.Prerequisites
- Install Dapr on Kubernetes
- Access to a Dynatrace tenant and an API token with
openTelemetryTrace.ingest,metrics.ingest, andlogs.ingestscopes - Helm
Set up Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector to push to your Dynatrace instance
To push traces to your Dynatrace instance, install the Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector on your Kubernetes cluster.
Create a Kubernetes secret with your Dynatrace credentials:
kubectl create secret generic dynatrace-otelcol-dt-api-credentials \ --from-literal=DT_ENDPOINT=https://YOUR_TENANT.live.dynatrace.com/api/v2/otlp \ --from-literal=DT_API_TOKEN=dt0s01.YOUR_TOKEN_HEREReplace
YOUR_TENANTwith your Dynatrace tenant ID andYOUR_TOKEN_HEREwith your Dynatrace API token.Use the Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector distribution for better defaults and support than the open source version. Download and inspect the
collector-helm-values.yamlfile. This is based on the k8s enrichment demo and includes Kubernetes metadata enrichment for proper pod/namespace/cluster context.Deploy the Dynatrace Collector with Helm.
helm repo add open-telemetry https://open-telemetry.github.io/opentelemetry-helm-charts helm repo update helm upgrade -i dynatrace-collector open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector -f collector-helm-values.yaml
Set up Dapr to send traces to the Dynatrace Collector
Create a Dapr configuration file to enable tracing and send traces to the OpenTelemetry Collector via OTLP.
Update the following file to ensure the
endpointAddresspoints to your Dynatrace OpenTelemetry Collector service in your Kubernetes cluster. If deployed in thedefaultnamespace, it’s typicallydynatrace-collector.default.svc.cluster.local.Important: Ensure the
endpointAddressdoes NOT include thehttp://prefix to avoid URL encoding issues:apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1 kind: Configuration metadata: name: tracing spec: tracing: samplingRate: "1" otel: endpointAddress: "dynatrace-collector.default.svc.cluster.local:4318" # Update with your collector's service addressApply the configuration with:
kubectl apply -f collector-config-otel.yaml
Deploy your app with tracing
Apply the tracing configuration by adding a dapr.io/config annotation to the Dapr applications that you want to include in distributed tracing, as shown in the following example:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
...
spec:
...
template:
metadata:
...
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/app-id: "MyApp"
dapr.io/app-port: "8080"
dapr.io/config: "tracing"
Note
If you are using one of the Dapr tutorials, such as distributed calculator, you will need to update theappconfig configuration to tracing.You can register multiple tracing exporters at the same time, and the tracing logs are forwarded to all registered exporters.
That’s it! There’s no need to include any SDKs or instrument your application code. Dapr automatically handles the distributed tracing for you.
View traces
Deploy and run some applications. After a few minutes, you should see traces appearing in your Dynatrace tenant:
- Navigate to Search > Distributed tracing in your Dynatrace UI.
- Filter by service names to see your Dapr applications and their associated tracing spans.
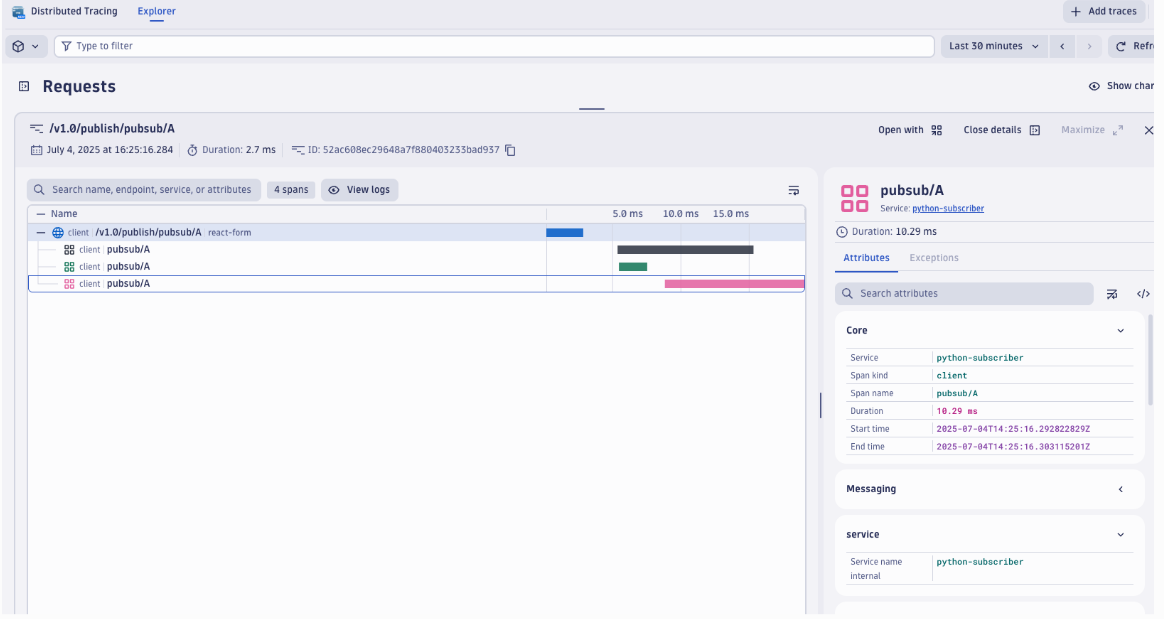
Note
Only operations going through Dapr API exposed by Dapr sidecar (for example, service invocation or event publishing) are displayed in Dynatrace distributed traces.Disable OneAgent daprd monitoring
If you are running Dynatrace OneAgent in your cluster, you should exclude the daprd sidecar container from OneAgent monitoring to prevent interferences in this configuration. Excluding it prevents any automatic injection attempts that could break functionality or result in confusing traces.
Add this annotation to your application deployments or globally in your dynakube configuration file:
metadata:
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/app-id: "MyApp"
dapr.io/app-port: "8080"
dapr.io/config: "tracing"
container.inject.dynatrace.com/daprd: "false" # Exclude dapr sidecar from being auto-monitored by OneAgent
Related links
- Try out the observability quickstart
- Learn how to set tracing configuration options
- Dynatrace OpenTelemetry documentation
- Enrich OTLP telemetry data with Kubernetes metadata